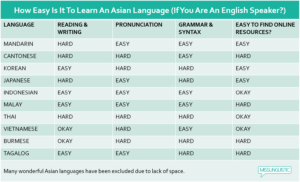
Malay is considered a relatively easy language to learn, especially for English speakers. It features a straightforward pronunciation and a non-complex grammar structure.
Learning Malay offers a gateway to a rich cultural tapestry, found in countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, and Brunei. With its roots in the Austronesian language family, Malay boasts a logical spelling system that is largely phonetic, making reading and writing more accessible for beginners.
The language employs a Latin alphabet, which is familiar to those acquainted with Western languages, thereby reducing the initial learning curve. Embarking on the journey of mastering Malay exposes learners to various dialects, though the standardized form, Bahasa Malaysia, is widely taught and understood. Vocabulary in Malay often incorporates words borrowed from languages such as Arabic, Sanskrit, and English, offering cognates that facilitate easier memorization for learners. Cultural immersion, consistent practice, and engagement with native speakers can further streamline the learning process, making it an achievable endeavor for anyone interested in embracing this linguistic venture.
Introduction To The Malay Language
Discovering Malay entails embarking on a journey rich with cultural ties and linguistic structure. As a language, Malay presents both intriguing aspects and achievable challenges for language enthusiasts. This section explores what makes Malay a unique and significant language on the global stage and how its historical roots have shaped the modern dialects we encounter today.
Global Significance
Malay is a linguistic bridge across nations. It is the national language of Malaysia, and an official language in Singapore, Indonesia, and Brunei. The language boasts over 200 million speakers. This cultural cornerstone captivates learners with its widespread use and influence in Southeast Asia.
It holds a pivotal role in ASEAN communication, establishing itself as a key player in regional diplomacy and international affairs. The growth of the Southeast Asian economy enhances its global importance every year.
Historical Context
Malay’s roots trace back to the Austronesian family. It began as a trading language in the Malay Archipelago, simplifying interactions among diverse ethnicities. Its rich history reflects through a tapestry of colonial influences from nations like Portugal, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
- 7th Century: Old Malay emerges in inscriptions.
- 15th-19th Century: Becomes lingua franca of the Malacca Sultanate and beyond.
- 20th Century: Standardization and adoption as national languages in several countries.
Today, the Malay language reflects a journey through time, carrying elements of its interactions with other cultures and languages. Understanding this history enriches the learning process, making it more than just acquiring a means of communication.
Key Features Of Malay
The Malay language, a key to Southeast Asia’s cultural door, presents unique features that make it a fascinating study. Whether you’re traveling or expanding your linguistic skills, unraveling the puzzle of Malay starts with understanding its core elements. Let’s explore the key features of the Malay language, from its straightforward alphabet to its practical phrases.
Alphabet And Pronunciation
Malay uses the Latin alphabet, similar to English. This aspect makes it accessible for learners familiar with the Latin script. The alphabet consists of 26 letters, with a few pronunciation nuances that are easy to grasp.
Pronunciation in Malay is phonetic and consistent. Each letter has a single sound and there are no silent letters. This clarity simplifies learning and speaking. Here’s a brief overview:
| Letter | Sound |
|---|---|
| A | Like ‘a’ in “father” |
| E | Similar to ‘e’ in “bed” |
Grammatical Structure
The grammatical structure of Malay is simple and straightforward. Nouns have no gender and there are no articles like ‘the’ or ‘a’. Verbs don’t conjugate based on tense, which means fewer rules to remember.
- No plurals – Repeat the noun for plurality.
- Tenses – Indicated by time markers, not verb changes.
- Word order follows the Subject-Verb-Object format, similar to English.
Common Phrases
Everyday communication in Malay involves a set of handy phrases. Learning these can help you navigate basic conversations with ease. Here are a few to get started:
- Selamat pagi – Good morning
- Terima kasih – Thank you
- Maaf – Sorry Add more items as necessary
The Challenge Of Learning Malay
Embarking on the journey of learning Malay offers unique challenges. A language spoken by millions, its reputation varies. Is it truly a tough nut to crack?
Myths Vs. Reality
Common misconceptions about Malay may intimidate learners. The reality, however, often paints a different picture. Malay uses Latin script, simplifying the reading process for those familiar with the English alphabet.
- No tones or gendered nouns ease the learning curve.
- Grammatical rules are often more straightforward than other languages.
But let’s not underestimate the effort required. Mastery demands commitment and practice.
Potential Difficulties For Learners
Every language has its hurdles. Here’s what learners might find tricky:
| Aspect | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary | Unique words with no English equivalent |
| Pronunciation | Sounds rarely found in English |
| Grammar | Affixes altering word meaning |
| Context | High reliance on context for meaning |
Despite these potential roadblocks, resources are aplenty. Structured courses, apps, and language groups offer support.
- Engage with native speakers for authentic exposure.
- Immerse in culture to enhance understanding and retention.
- Practice consistently to overcome challenges.
Credit: misslinguistic.com
Cultural Nuances In Malay
Understanding the cultural nuances of Malay adds another layer to the language learning journey. As you delve into Malay, it goes beyond just words and grammar. The cultural context shapes the language and its use in conversation. Acknowledging cultural nuances helps learners grasp the true essence of Malay, enhancing conversations with native speakers. Let’s explore these nuances, particularly the role of honorifics and non-verbal communication.
Role Of Honorifics
Honorifics play a pivotal role in Malay conversation, often indicating respect and social hierarchy. Mastering this aspect is essential. It shapes interactions and displays cultural understanding. Here’s a glimpse into their usage:
- ‘Datuk’/‘Datin’ – titles for distinguished individuals;
- ‘Encik’/’Puan’ – formal address for men/women respectively;
- ‘Kakak’/’Abang’ – refers to older sister/brother in a familial or informal context.
These words precede names, ensuring conversations maintain a respectful tone and adhere to cultural expectations.
Non-verbal Communication
Malay speakers rely heavily on non-verbal cues, including gestures, expressions, and body language. Aspects of non-verbal communication can convey politeness or disapproval without being vocal. Understanding these can prevent miscommunications. Consider these non-verbal norms:
| Gesture | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Smiling | Conveys friendliness and ease; |
| Nodding | Indicates agreement or understanding; |
| Avoiding eye contact | Signals respect, especially towards elders. |
Effective communication in Malay involves tuning into these physical signals as much as verbal ones.
Resources For Learning Malay
Are you eager to tackle the Malay language? Good news! A wealth of resources is available to guide you on this linguistic journey. Whether through online platforms or in-person language schools, each resource brings you a step closer to fluency. Let’s explore these tools designed to make learning Malay accessible and enjoyable.
Online Platforms
Embracing technology, numerous online platforms offer Malay language courses. These websites and apps provide interactive lessons, games, and quizzes to enrich your learning experience.
- Duolingo – Features a game-like environment for easy learning.
- Babbel – Delivers personalized review sessions.
- italki – Connects you with native speakers for language practice.
Additionally, engaging in forums and chat groups can greatly enhance your language skills.
Language Schools And Courses
For those who prefer a traditional classroom setting, language schools offer structured courses in Malay. Instructors proficient in the language provide individual attention and help with pronunciation.
| School Name | Location | Course Types |
|---|---|---|
| ILC Singapore | Singapore | Group, Private |
| University of Malaya | Kuala Lumpur | Intensive, Part-time |
| YMCA Language School | Various locations | Regular, Crash courses |
Remember, immersing yourself in the culture and practicing consistently are key to mastering Malay.

Credit: ling-app.medium.com
Methods To Enhance Malay Proficiency
Learning Malay can be an adventure filled with new sounds, words, and expressions. To achieve fluency, learners can use a variety of methods. These strategies focus on different learning aspects. They make the journey enjoyable and effective.
Immersive Learning
Direct exposure to the Malay language is a powerful tool. Immersive learning means surrounding yourself with Malay. You can do this in many ways:
- Label household items with their Malay names.
- Switch your devices to the Malay language.
- Watch Malay movies and shows.
- Listen to Malay music and radio stations.
| Activity | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Watching Malay TV | Improves listening and understanding. |
| Reading Malay books | Enhances vocabulary and grammar skills. |
These activities foster language skills without feeling like study sessions.
Practice With Native Speakers
Interacting with native Malay speakers is crucial. This interaction sharpens pronunciation and speaking fluency. Here’s how you can engage:
- Join language exchange communities.
- Participate in Malay cultural events.
- Use language learning apps with Malay speakers.
Regular conversation with natives offers real-time feedback. It helps learners to correct mistakes immediately. Keep a notebook for new words and phrases. This habit makes remembering easier.
The Role Of Technology In Learning Malay
Becoming fluent in Malay does not have to be a daunting task. The right tools can make this journey fun and effective. Technology plays a crucial role. It helps learners engage with the Malay language in varied, interactive ways. Let’s dive into how technology is making learning Malay easier than ever.
Language Learning Apps
Apps turn learning Malay into a game. They are perfect for beginners. They often come with user-friendly interfaces. See how they make a difference:
- Interactive exercises: They make practice enjoyable.
- Progress tracking: Users see their improvements clearly.
- Customizable lessons: Learners focus on their weak areas.
- Accessibility: Learn anytime and anywhere with a mobile device.
Online Tutors And Communities
Personal guidance boosts language skills significantly. Online tutors provide one-on-one sessions. Communities offer practice with peers. See their impact:
- Native speaker interaction: Gain authentic pronunciation and usage.
- Immediate feedback: Correct mistakes quickly.
- Flexible scheduling: Fit learning into any lifestyle.
- Cultural insights: Understand the Malay culture through language exchanges.
Credit: ling-app.medium.com
Success Stories And Testimonials
Embarking on the journey to learn a new language often pairs with stories of triumph and sage advice from those who traversed the path before. Successful learners of Malay language share their experiences and testimonials, leaving crumbs of wisdom for future language adventurers. Dive into real-life accounts and absorb invaluable tips from seasoned polyglots on mastering Malay. Let’s explore these inspiring tales and expert insights.
Learners’ Experiences
Countless individuals from around the globe have tackled the rewarding challenge of learning Malay. Their stories shine with achievement and offer practical perspectives. Success in learning Malay often hinges on one’s dedication and the strategies employed. Here, learners recount their journeys in their own words:
- “Grasped the basics in just a few months!” – Emily, Australia
- “A supportive community made all the difference.” – Amir, Egypt
- “Interactive apps paved the way to my fluency.” – Sarah, Canada
These testimonials highlight diverse methodologies, from leveraging digital tools to immersing oneself in a supportive community. Each path tells a tale of dedication and the joy of acquiring a new linguistic skill.
Advice From Polyglots
Polyglots, with their wealth of language acquisition expertise, offer their best practices for mastering Malay. Their advice serves as a guiding beacon for new learners:
| Polyglot | Advice |
|---|---|
| Lukas | “Focus on Malay verbs early—the key to forming sentences.” |
| Maria | “Listen to local Malay radio daily for natural pronunciation.” |
| Jin | “Practice speaking from day one, even with mistakes.” |
These shards of wisdom are gleaned from years of language learning. They indicate a shared understanding that listening, practicing speaking, and a strong grasp of verbs can propel Malay language proficiency.
Conclusion: Embracing The Language Journey
Learning Malay opens a world not just of words, but of culture and connection. As we wrap up our journey, let’s focus on the positive aspects of becoming bilingual in Malay.
Benefits Of Bilingualism
- Sharper Brain: Studies show learning a new language boosts brain power.
- Better Opportunities: Knowing two languages opens up more job options.
- Cultural Insight: Speaking Malay immerses you into a rich culture.
- Travel Skills: Travel around Malaysia becomes easier and more fun.
Personal And Professional Growth
Personal growth blooms when you learn Malay. New friendships, understanding, and experiences await. Professional growth also leaps forward. With Malay, you stand out in the job market.
Becoming bilingual in Malay is a challenge worth taking. The benefits touch every part of life, building a bridge to new adventures. Embrace the journey and open doors to a whole new world.
Frequently Asked Questions On Is Malay A Hard Language To Learn
How Long Does It Take To Learn Malay?
Learning Malay varies per individual, typically taking a few months to a year for basic fluency. Regular practice and immersion can significantly reduce this time.
Is Malay Easy Or Hard To Learn?
Malay’s difficulty level varies based on your native language and language learning experience. Generally, its straightforward grammar and phonetic script make it relatively easier to learn for speakers of English and other Roman alphabet-based languages.
Is Malay Speaking Hard?
Learning Malay can be challenging for non-native speakers, but its straightforward grammar and phonetic spelling make progress easier. Regular practice and immersion enhance proficiency.
Is Malaysia A Hard Language To Learn?
Learning Malaysian, the primary language of Malaysia, varies in difficulty depending on the learner’s native language and language-learning background; speakers of related languages may find it easier to master.
Conclusion
Mastering Malay comes with its challenges, yet it’s an endeavor worth pursuing. With consistent practice and the right resources, learners can unlock a rich cultural tapestry through its phrases. Embrace the journey and watch your language skills flourish. Malay invites you with open arms.



